MGM4000 Portable High-Resolution Magnetic Gradiometer
Professional-Grade Geophysical Imaging System for Gold Exploration, Mineral Prospecting, Archaeology, Construction, and Void Detection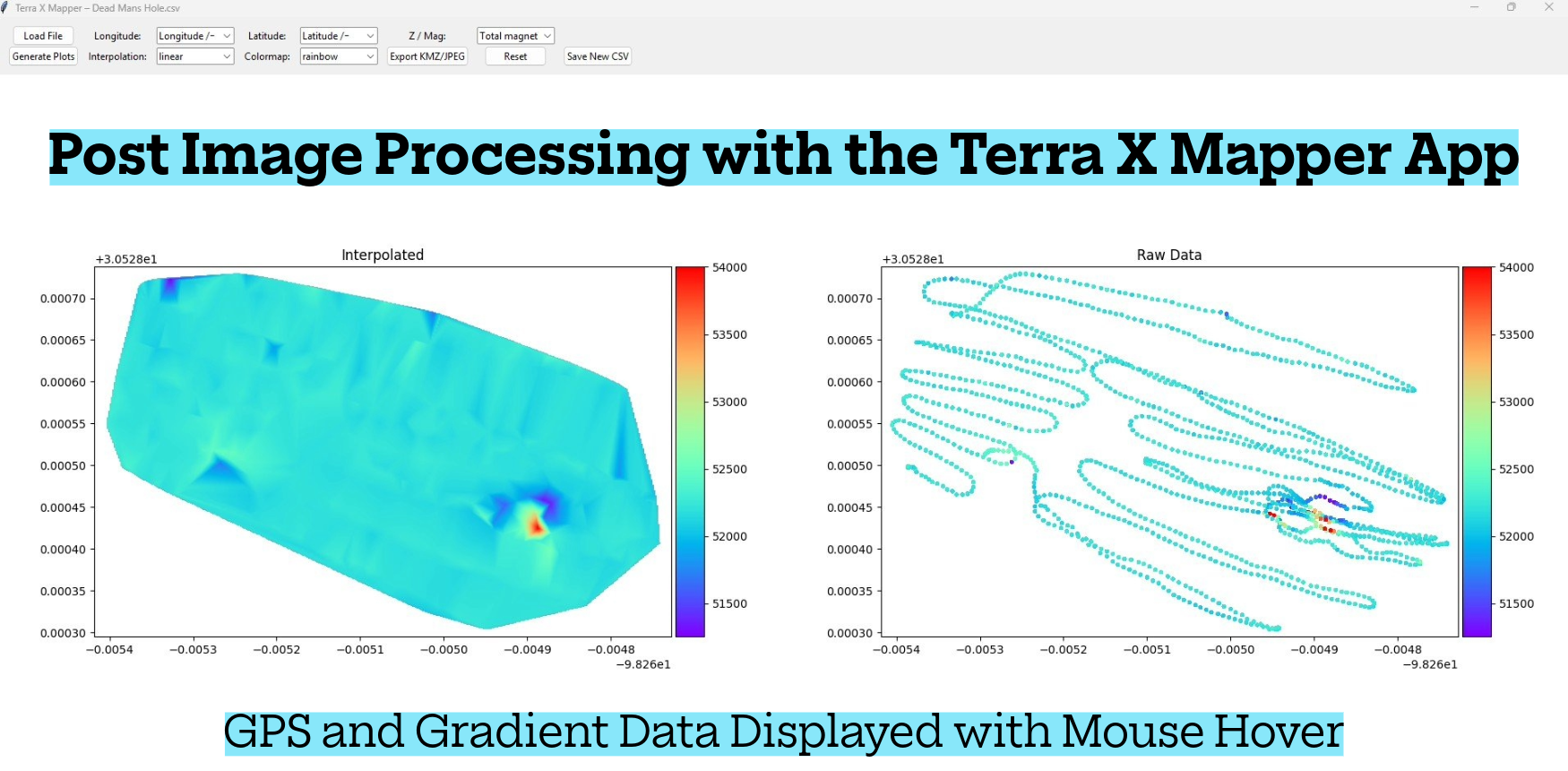
Product Overview
The MGM4000 is a portable, ground-based magnetic gradiometer designed for professionals who demand precision subsurface imaging beyond what traditional metal detectors can provide. Unlike conventional detectors that simply beep over targets, the MGM4000 maps underground geological structures, mineralization zones, buried features, and voids by measuring subtle variations in the Earth's magnetic field and displaying them as detailed visual maps in real-time.
This is not a point-detection device—it's a professional geophysical mapping instrument engineered to provide stable, repeatable gradient data for informed exploration and excavation decisions. Whether you're prospecting for gold, conducting archaeological surveys, planning construction projects, or searching for hidden voids and chambers, the MGM4000 reveals subsurface features that remain invisible to standard detection equipment.
Who Should Use the MGM4000?
Gold Prospectors & Mineral Explorers: Map buried paleo-channels, gold-bearing quartz veins, shear zones, and mineralized structures from 3-20 meters deep. The MGM4000 excels in highly mineralized soils and volcanic terrain where conventional detectors struggle.
Archaeologists & Historical Researchers: Locate buried foundations, walls, tombs, chambers, ancient structures, and disturbed ground with unprecedented clarity. The system detects both metallic and non-metallic archaeological features.
Civil Engineers & Construction Professionals: Identify subsurface voids, weak zones, buried utilities, old foundations, disturbed soil, and hidden obstacles before excavation begins. Essential for site planning, foundation assessment, and risk mitigation.
Treasure Hunters: Map buried caches, chambers, voids, and both magnetic and non-magnetic metals. The MGM4000 detects the disturbance left by burial—even when the metal itself produces minimal signal.
Water Well Contractors: Map fracture zones, fault-controlled aquifers, weathered bedrock, and buried paleo-channels that serve as productive groundwater targets.
Environmental & Geotechnical Consultants: Detect buried tanks, drums, infrastructure, and contamination-related features for site assessment and remediation planning.
How the MGM4000 Works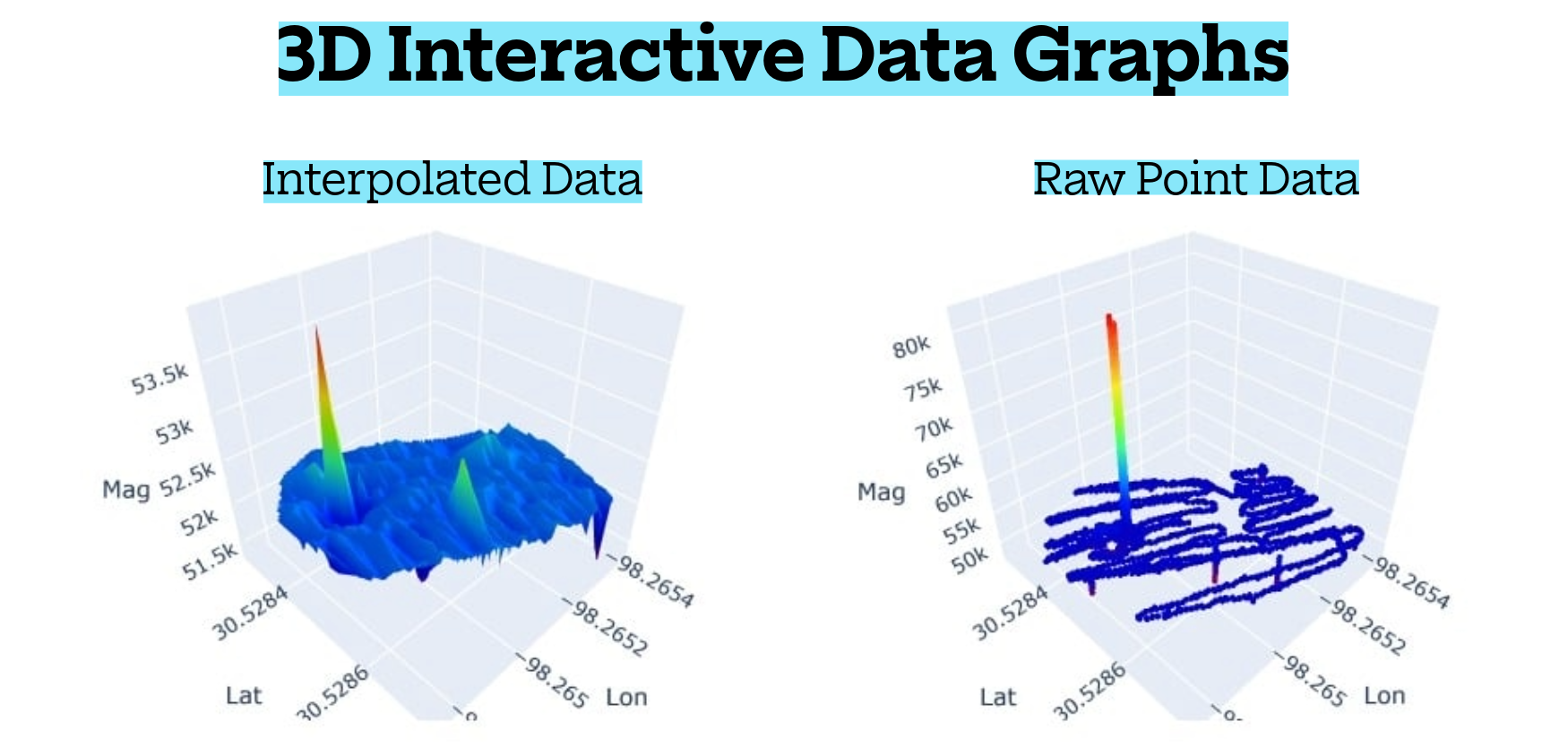
The MGM4000 operates as a passive geophysical imaging instrument—it does not transmit signals into the ground. Instead, it precisely measures natural variations in the Earth's magnetic field caused by subsurface features.
The Physics: Everything underground that differs magnetically from surrounding soil creates a subtle disturbance in the Earth's magnetic field. The MGM4000 employs dual low-SWaP magneto-inductive vector magnetic sensors in a fixed-baseline gradiometer configuration to measure first-order magnetic field gradients. By comparing measurements taken at slightly different positions as you walk survey grids, the system identifies patterns that reveal:
- Sharp gradients → Compact objects or man-made features
- Broad, smooth anomalies → Geological structures like veins or altered zones
- Linear trends → Faults, dikes, walls, tunnels, or paleo-channels
- Void signatures → Missing mass from caves, chambers, or tombs
Real-Time Mapping: Data is displayed instantly as color-coded heatmaps, contour maps, profile lines, and depth-related anomaly indicators. You see exactly where anomalies are located, their size, depth characteristics, and spatial behavior—no guesswork, no unreliable audio tones.
 Depth Estimation: Depth comes from physics, not arbitrary guessing. The system analyzes anomaly strength, field change rate, and disturbance width to estimate target depth. Shallow objects produce sharp, intense signals while deeper targets generate broader, smoother signatures.
Depth Estimation: Depth comes from physics, not arbitrary guessing. The system analyzes anomaly strength, field change rate, and disturbance width to estimate target depth. Shallow objects produce sharp, intense signals while deeper targets generate broader, smoother signatures.
Key Applications & Detection Capabilities
Gold & Mineral Exploration (Depth: 3-20m depending on geology)
Alluvial/Placer Gold Systems:
- Buried ancient river channels (paleo-channels)
- Heavy-mineral traps and gravel lenses
- Dense material accumulations beneath overburden
- Linear or sinuous anomalies following old river paths
Gold-Bearing Quartz Veins:
- Iron-rich alteration zones around veins
- Sulfide and magnetite associations
- Narrow, linear anomalies with consistent directional trends
- Helps you follow the vein, not just hit random spots
Shear Zones & Fault-Controlled Gold:
- Structural breaks in bedrock
- Magnetically altered surrounding rock
- Broad linear features and parallel structures
- Ideal for identifying deep-rooted systems before drilling
Hard-Rock/Lode Gold Systems:
- Altered host rock footprints
- Iron-bearing minerals around gold zones
- Structural intersections indicating mineralization
- Large anomaly patterns showing depth and intensity
Construction & Civil Engineering (Depth: 0-20m)
Site Planning & Ground Condition Assessment:
- Disturbed or filled ground
- Soil transitions and compaction differences
- Hidden voids or weak zones
- Clear contrast mapping between competent and compromised ground
Foundations & Structural Planning:
- Old footings or buried slabs
- Backfilled excavations
- Voids or poorly compacted zones
- Reduces settlement, cracking, and differential movement risk
Roads, Highways & Infrastructure:
- Soft subgrade zones
- Buried debris or trenches
- Old roadbeds beneath new construction
- Prevents subsidence and premature pavement failure
Utilities & Buried Infrastructure:
- Metallic pipes and tanks
- Trenches and disturbed ground
- Septic systems and leach fields
- Prevents accidental utility strikes and costly delays
Void Detection (Depth: 2-20m)
Natural Caves & Karst Cavities:
- Air-filled or partially collapsed cavities
- Altered rock around cave boundaries
- Particularly effective for buried caves with no surface opening
Abandoned Mines & Tunnels:
- Old shafts, horizontal adits, and chambers
- Timbered or stone-lined voids
- Collapse zones and disturbed rock
- Excellent for hazard detection and safety surveys
Tombs, Burial Chambers & Crypts:
- Chamber voids with stone linings
- Rectangular, circular, or oval geometric shapes
- Backfilled access shafts
- One of the most distinctive and interpretable void targets
Chultuns, Cisterns & Storage Chambers:
- Bell-shaped cavities and access shafts
- Circular footprints with strong central contrast
- Ancient subterranean storage features
Treasure Hunting (Depth: 0-20m)
Voids & Hidden Chambers:
- Air-filled or loosely filled cavities
- Old tunnels, cellars, and hiding places
- Strong contrast with surrounding ground
- Many historic treasures were hidden inside voids
Backfilled Pits & Disturbed Ground:
- Compaction differences from excavation
- Burial signatures even when metal is gone
- Clear contrast with undisturbed ground
Non-Magnetic Metals (Gold, Silver, Coins):
- Detects excavation disturbance, not just the metal
- Finds the hiding place when metal detectors fail
- Works for caches buried in chambers or soil
Magnetic Metals (Iron Chests, Weapons):
- Sharp, high-contrast magnetic spikes
- Iron-bound chests and hardware-rich hoards
- Military caches and buried tools
Water Exploration (Depth: 5-20m)
Fracture Zones & Fault-Controlled Aquifers:
- Fractured rock zones and fault damage halos
- Altered, moisture-hosting rock
- Linear or branching anomaly patterns
- Higher-yield, longer-lasting well targets
Weathered Bedrock Aquifers:
- Transition from solid to weathered bedrock
- Porous zones holding water
- Clear contrast with fresh bedrock
Buried Paleo-Channels:
- Ancient river channels beneath cover
- Channel geometry and dense gravel layers
- Prime targets for high-yield wells in arid regions
Technical Specifications
 Sensor Technology
Sensor Technology
- Sensor Type: Dual Low-SWaP Magneto-Inductive Vector Magnetic Sensors
- Measurement Axes: Three-axis (X, Y, Z)
- Operating Principle: Magneto-inductive resonance frequency shift proportional to ambient magnetic field intensity
- Configuration: Fixed horizontal dual-sensor magnetic gradiometer
- Baseline: 0.50 meters
- Gradient Order: First-order magnetic field gradient
- Typical Sensor Height: 20-25 cm above ground
Magnetic Performance
- Magnetic Field Measurement Range: ±65,000 nT (Earth field compatible)
- Magnetic Resolution: ≤ 0.01 nT
- Noise Floor (typical): < 0.05 nT RMS during walking surveys
- Gradient Resolution: ≤ 0.02 nT/m
- Dynamic Range: 130 dB
Sampling & Data Acquisition
- Internal Sensor Sampling Rate: 4,000 samples per second (4 kHz) per sensor
- Sensor Synchronization: Hardware-synchronized dual-sensor acquisition
- Survey Output Rate: 10 Hz (10 fully processed gradient measurements per second)
- Temporal Resolution: 100 ms per output sample
- Data Continuity: Continuous streaming during walking surveys
This high-rate oversampling configuration provides exceptional instantaneous sensitivity while maintaining stable gradient measurements during operator motion, ensuring consistent spatial sampling at typical walking speeds.
Depth Sensitivity (Geology Dependent)
Target depth capability depends on size, magnetic susceptibility contrast, geometry, and background geology:
- Narrow mineralized structures: ~3-8 m
- Broad altered zones and shear systems: ~8-15 m
- Large iron-rich geological bodies: Up to ~20 m
- Targets deeper than ~30 m: Outside intended operating envelope
Positioning & Orientation
- Positioning: Integrated GNSS for georeferenced data acquisition
- Orientation Compensation: Integrated inertial sensing for tilt correction
- Heading Reference: GNSS-assisted directional alignment
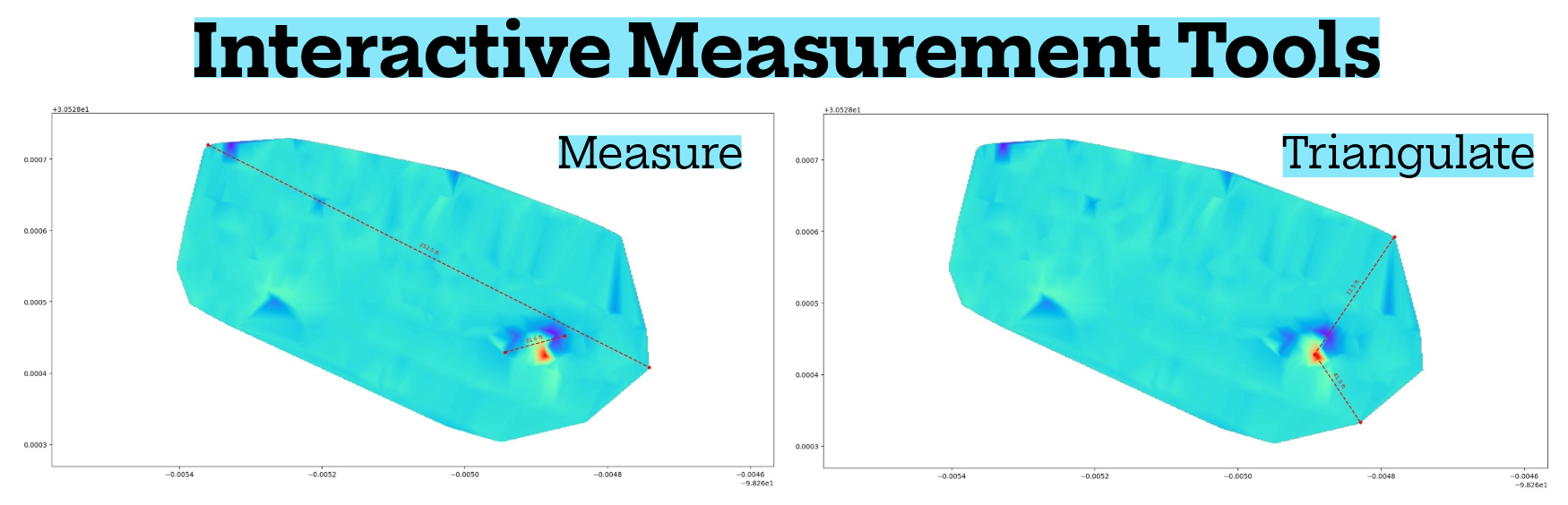
Data Output & Visualization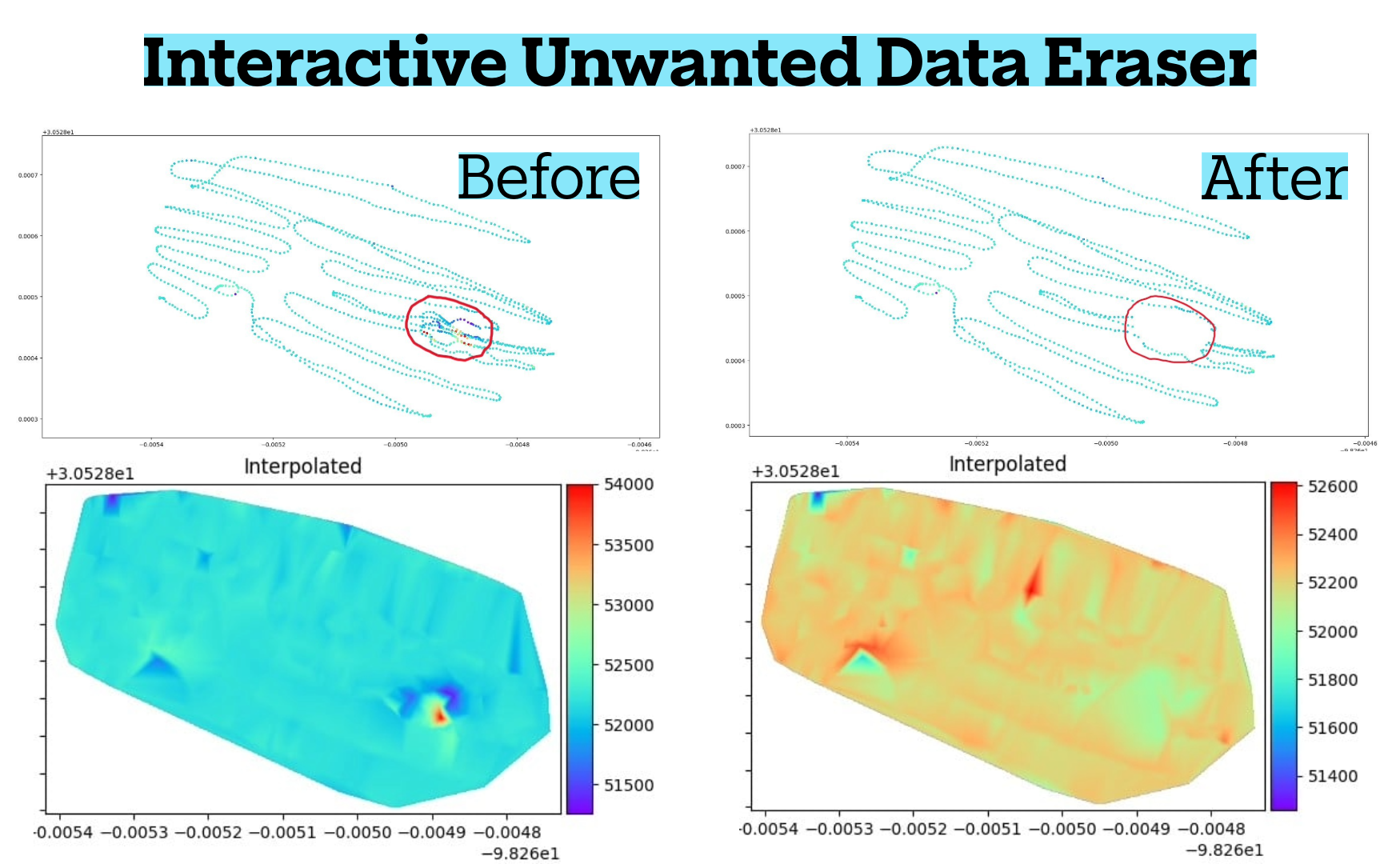
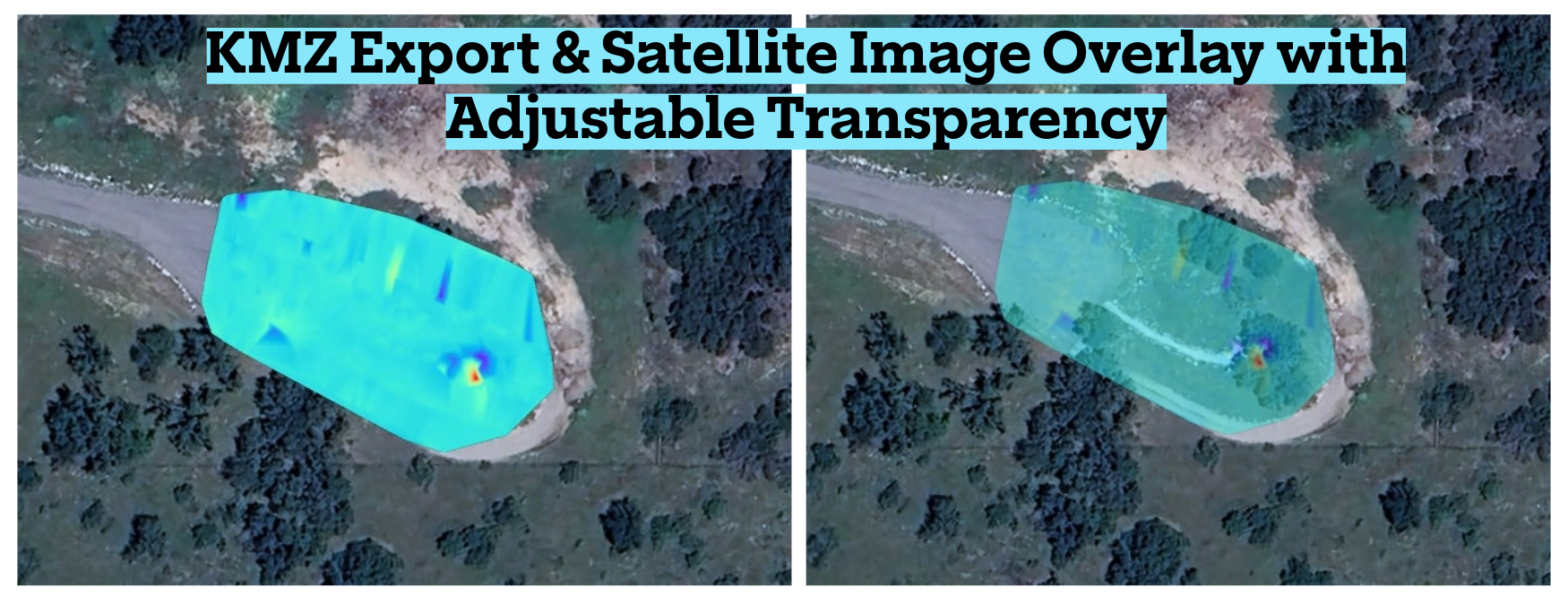
- Real-Time Outputs: Magnetic gradient values, continuous line profiles, live 2D heatmap visualization
- Export Formats: CSV, GIS-compatible formats (KMZ)
- Interpretation Focus: Gradient geometry, continuity, and structural coherence
Survey Operation
- Survey Mode: Continuous walking surveys
- Typical Walking Speed: ~0.5-1.0 m/s
- Spatial Sampling (at 1 m/s): ~0.10 m per sample at 10 Hz
- Survey Control: Manual or GPS-guided grid acquisition
What's Included
Contact Kellyco at (888) 535-5926 for complete package details, accessories, and configuration options tailored to your specific application needs.
Physics-Based Limitations (What the MGM4000 Cannot Do)
Transparency is important. The MGM4000:
- Does not directly detect non-magnetic materials lacking magnetic susceptibility contrast
- Requires target materials or surrounding geology to differ magnetically from background
- Not suitable for heavily metal-contaminated environments with excessive magnetic debris
- Not intended for deep exploration targets beyond ~30 meters
- Performance depends on soil type, target size, and geological conditions



 Depth Estimation: Depth comes from physics, not arbitrary guessing. The system analyzes anomaly strength, field change rate, and disturbance width to estimate target depth. Shallow objects produce sharp, intense signals while deeper targets generate broader, smoother signatures.
Depth Estimation: Depth comes from physics, not arbitrary guessing. The system analyzes anomaly strength, field change rate, and disturbance width to estimate target depth. Shallow objects produce sharp, intense signals while deeper targets generate broader, smoother signatures. Sensor Technology
Sensor Technology